- Bulgaria-Italy-Spain supercapacitors



B. Mladenova1 , S. Veleva1, T. Stankulov1 , M. Matrakova1 , A. Aleksandrova1 , B. Karamanova1 , A. Arenillas2 , A. Stoyanova1 , B. Tsintsarski3
1Institute of Electrochemistry and Energy Systems Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, G. Bonchev Str. 10, Sofia, Bulgaria
2Instituto de Ciencia y Tecnología del Carbono , INCAR CSIC. Francisco Pintado Fe, 26, 33011, Oviedo, Spain
3Institute of Organic Chemistry with Centre of Phytochemistry Bulgarian Academy of Sciences, G. Bonchev Str. 9, Sofia, Bulgaria
email: borislava.mladenova@iees.bas.bg
INTRODUCTION
Carbon xerogels are widely used as electrode materials and additives in electrochemical power sources. Their textural and structural characteristics can be controlled according to the synthesis conditions which make it possible to adapt their properties according to specific applications.
In the present study are shown the results of research carried out on the synthesis of carbon xerogels prepared by thermal treatment in microwave oven (AXGO) and in vacuum dryer (RFCA) synthesis based on resorcinol and formaldehyde. The obtained carbon materials were characterized using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) X-ray diffraction (XRD) and specific surface determination (BET). The obtained carbon materials were used as additives in negative electrode mass of lead acid batteries.
EXPERIMENTAL
Synthesis of xerogels
Two organic xerogels were synthesized by the polycondensation of using resorcinol (99 purity) and formalin 37% solution (purity) as reactants, deionized water as solvent, and a solution of NaOH (purity) as basification agent. The gelation, curing and drying of the gel is done by heating. The resulting organic xerogel is subjected to a high
temperature treatment at 1000°C for carbonization and activation.
Design of small leadacid cell
Electrode preparation
0.8 % BaSO4 of the weight of leady oxide (LO)
0.2 % LignoSulfonate (LS) of the weight of LO
0.5 % RFCA of the weight of LO
0.25 % AXGO of the weight of LO
0.0 % Carbon additive (control sample)
Assembly of 2.0V /115mAh
Cell testing setup
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
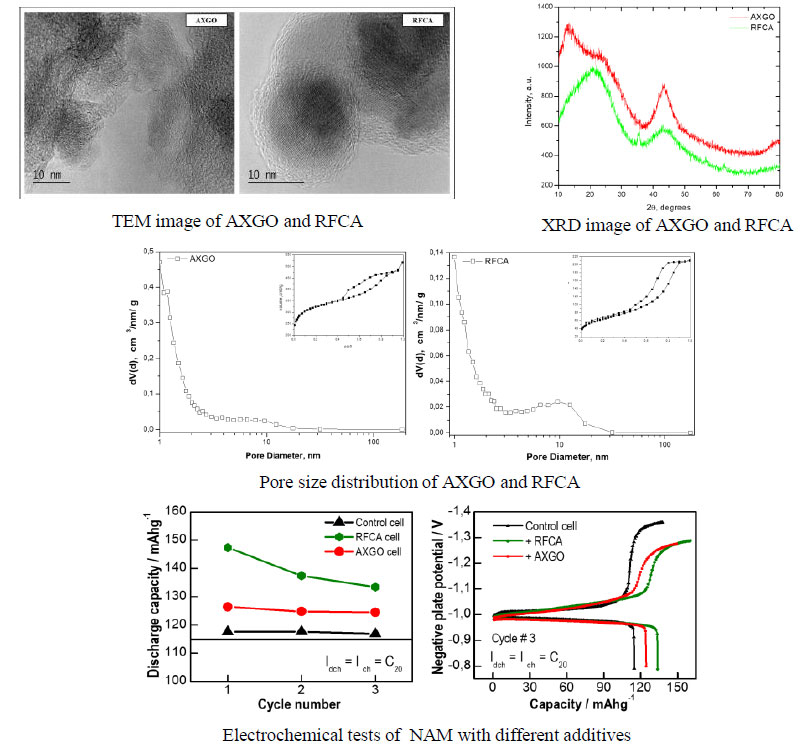
SUMMARY
- The discharge capacity of the control electrode is 117 mAhg-1, while that of the electrode with + 0.5 RFCA additive is 134 mAhg-1, or + 0.25% AXGO electrode has a capacity of 125 mAhg-1.
- NAM formulation with carbon additive exhibit positive effect on the discharge capacity of the lead cells.
These are initial studies and the results obtained are a good prospect for future work in this area.
Acknowledgement: This research is supported by the award № DO1-286 / 07.10.2020 granted from by the Ministry of Education and Science of Bulgaria. Authors gratefully acknowledge.
Additional information can be found HERE.